Doctors use UV light therapy to treat various common skin conditions, such as psoriasis and eczema. They consider it effective and safe, although it may cause short- and long-term side effects, including itching and wrinkling.
UV light therapy is not safe for everyone, such as people with a history of skin cancer or those with fair skin who develop sunburn easily.
This article examines UV light therapy, including its uses, types, side effects, and the conditions for which it is unsafe. It also discusses devices that provide therapy at home and what to expect from sessions in a clinic.
What is UV light therapy good for?
UV light therapy — also called phototherapy — involves the administration of UV radiation to treat various skin conditions. The radiation is a form of energy that scientists measure on a scale called the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. UV radiation is the portionTrusted Source of the EM spectrum between visible light and X-rays.
Doctors consider the therapy safe and effective for specific uses. It plays a major role in dermatology, the field of medicine that treats skin conditions. The most frequentTrusted Source uses include:
Psoriasis: This is an autoimmune condition that accelerates the growth cycle of skin cells. Autoimmune means a person’s immune system attacks their own tissues. Psoriasis is the most commonTrusted Source use of the therapy.
Long-term or chronic eczema: Eczema — also called atopic dermatitis — is an inflammatory skin condition. The therapy may be effective for certain types of eczema when other treatments do not produce satisfactory results or are inappropriate.
Mycosis fungoides: This is a condition where T-cell lymphocytes — a type of white blood cell — become cancerous and affect the skin. The therapy can cause inflammation in the early stages, but it subsides without needing to stop treatment sessions.
Vitiligo: This is an autoimmune condition where patches of skin lose pigment. When cases do not respond to topical treatment, UV light therapy is frequently a second-line treatment choice. Topical refers to the application of creams that contain medication to the skin.
Generalized lichen planus: This is an inflammatory autoimmune condition that affects the skin. Doctors consider UV light therapy a good option when people do not respond to systemic immunosuppressive therapy, medications that tamp down the immune system.
Polymorphic light eruption: This condition causes a rash in response to exposure to sunlight. UV light therapy is effective but can produce a rash in 50% of individuals. However, this is manageable with the use of topical medications.
Cutaneous graft-versus-host disease: This skin condition may occur in response to a type of stem cell transplant. It responds to some types of UV light therapy.
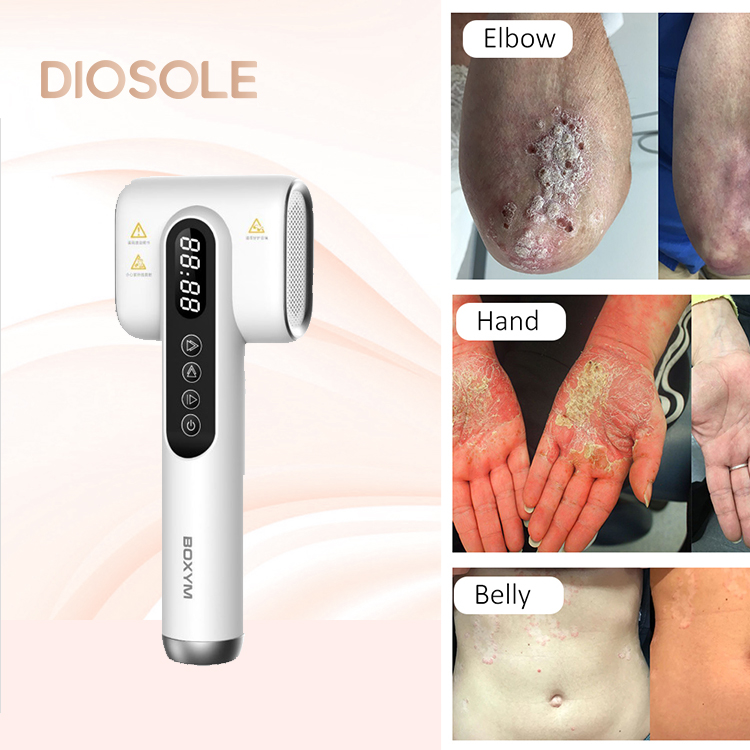
Home UV light therapy devices
Home UV light therapy is a relatively safe and effective self-treatment for certain skin conditions. An experienced doctor should supervise someone using these types of home devices, but not all dermatologists consent to do this due to the potential for side effects.
Some devices that deliver UV light therapy involve walk-in units for the whole body. Other devices entail tabletop or hand-held models for spot treatment.
Evidence from 2021Trusted Source suggests that home treatment has downsides, such as difficulty managing session duration and equipment. A lack of cost reimbursement from health insurers is an additional issue.